HCP Coverage Analysis Using 2D Western Blot

2D Western Blot Overview
Biologic drugs are subject to unique regulatory and technical requirements because of their origin and expression in genetically engineered host cells, as well as their underlying physicochemical properties and elaborate purification processes. One such requirement is the accurate monitoring and effective removal of process-derived impurities such as host-cell proteins (HCPs) and DNA/RNA, viruses, cell culture media, chromatographic leachates, and so on. Of these impurities, HCPs are perhaps the most challenging to accurately monitor. Each expression system’s proteome consists of thousands of different proteins, some of which can copurify with a biological drug, so the HCP monitoring method must be a multianalyte assay that can detect a great majority of the protein impurities that could ever be present in a batch of drug substance.
2D Western blotting is the current gold standard procedure for determining HCP coverage for biopharmaceutical product approval. It combines total protein detection with the use of specific HCP antibodies in high-resolution imaging. 2D Western blots can also be used to visualize post-translational protein modifications such as phosphorylation using anti-phospho antibodies.
The First Step of a 2D Western Blot: Protein Separation by IEF and SDS-PAGE
In the initial phase of a 2D Western blot, proteins are separated in two dimensions based on their isoelectric point (isoelectric focusing, IEF) and molecular weight (SDS-PAGE). This gel can be stained to visualize total protein, facilitating differential protein analysis. Additionally, individual protein spots can be excised directly from the gel for mass spectrometry identification.
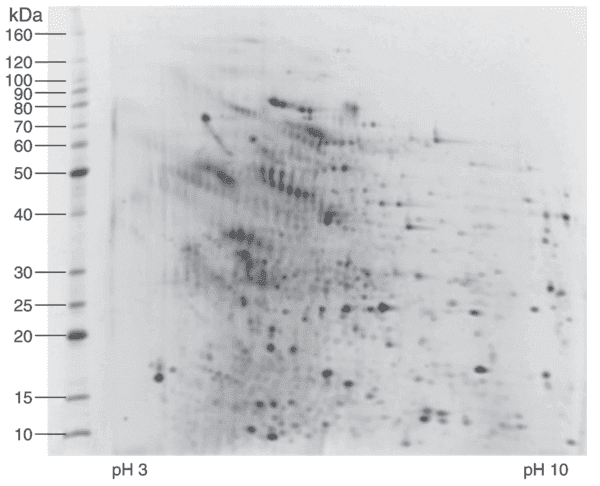
Fig 1. 2D IEF/SDS-PAGE analysis of representative CHO HCP calibration standard stained with a sensitive fluorescent stain.
The Second Step of a 2D Western Blot: Protein Transfer and Staining in 2D Gel Electrophoresis
Following 2D gel electrophoresis, proteins are transferred onto a PVDF membrane and stained using a high-specificity anti-HCP antibody. A secondary antibody, conjugated with either HRP (horseradish peroxidase) or a fluorescent dye, enhances detection sensitivity. This method is crucial for protein identification, HCP analysis, and Western blot applications, ensuring precise results in biopharmaceutical research.

Fig 2. Western blot analysis of the same gel shown in Fig 1.
Third Step: Conventional Coverage Analysis Using SpotMap Software
In a conventional coverage analysis, total protein from the in-gel stain is automatically and accurately overlayed with the immunostained Western blot. The accuracy of the software used and the skill of the operator all influence the accuracy and reliability of your coverage score so it’s imperative to use the latest, most modern technology available like the next-generation algorithms developed by TotalLab included in our SpotMap software.

Step 4 (optional): 2D Differential In Blot Electrophoresis (2D-DIBE) Coverage Analysis Using SpotMap Software
2D-DIBE (also known as 2D-DIGE) utilizes a fluorescent multiplexing approach where the proteins and antibodies are tagged with different cyanine dyes which respond to different wave. Total protein and antibody coverage can be analyzed on the same membrane. This method thereby bypasses the need for an alignment step (Gel to WB) leading to higher accuracy. Our SpotMap software also supports images obtained using 2D-DIGE or 2D-DIBE techniques.
Host Cell Protein Analysis Technique Comparison:
| ELISA | Standard 2D Western Blot | 2D DIGE Western Blot | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of gels for each Ab | N/A | Two | One |
| Detection Method | Colorimetric | Silver Staining | CyDye Labeling |
| Detect HCP Composition | No | Yes | Yes |
| Detect protein modification | No | Yes | Yes |
| Detect protein degradation | No | Yes | Yes |
| Protein and WB in same gel | No | No | Yes |
| In-gel protein and WB comparison | No | No | Yes |
| Accuracy | Low | Low | High |
| Inaccurate: In-direct reaction of antibodies with the antigen’s associated proteins | Inaccurate: Protein spots counted from the gel, NOT from membrane | Accurate: Protein spots counted directly from the membrane | |
False negative:
|
Error caused by:
|
Accurate:
|
|
| Consistency & Reproducibility | Lower | Lower | Higher |
