What Are Host Cell Proteins (HCPs) and Why Is Their Analysis Critical in Biologics?

Understanding Host Cell Proteins in Biopharmaceutical Production
Host cell proteins (HCPs) are process-related impurities generated during the manufacture of biopharmaceuticals. These proteins, originating from host cells such as CHO (Chinese Hamster Ovary) or E. coli, can persist through downstream processing and impact the safety, efficacy, and stability of biologics. HCPs are commonly introduced during harvesting steps when host cell lysis occurs and HCPs can even bind to and be copurified with target molecules like monoclonal antibodies or recombinant proteins (so called “hitchhiker” HCPs).
Even trace amounts of HCPs in therapeutic products can provoke immunogenic responses or degrade the drug substance, contributing to toxicity or reduced therapeutic effectiveness and shelf life. Consequently, regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EMA classify HCPs as a critical quality attribute (CQA), requiring rigorous monitoring throughout drug development and production.
Analytical Techniques for HCP Detection
HCP analysis and tracking is critical during the development of biopharmaceutical products for therapeutic purposes and involves both HCP quantification and detection using either (or a combination of) immuno-specific (such as ELISA) and nonspecific techniques (such as 2D-HPLC and 2D-DIGE).
To comply with regulatory expectations and ensure product safety, scientists apply a range of analytical tools for HCP analysis:
HCP-ELISA:
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a widely used technique for analyzing host cell proteins (HCPs). ELISAs are employed at various stages of biotherapeutic production to accurately quantify HCP levels and the data obtained from these assays is mandatory for regulatory filings with the FDA or EMA. ELISA’s can be customized to suit specific requirements or processed and the assay can be easily automated for high-throughput analysis using something like our SpotMap ELISA software.
The host cell protein ELISA technique provides a high-throughput, sensitive technique that can be used routinely throughout process development. Customized anti-HCP antibodies allow the user to quantify total HCP load and support batch-to-batch consistency during product development and process control.
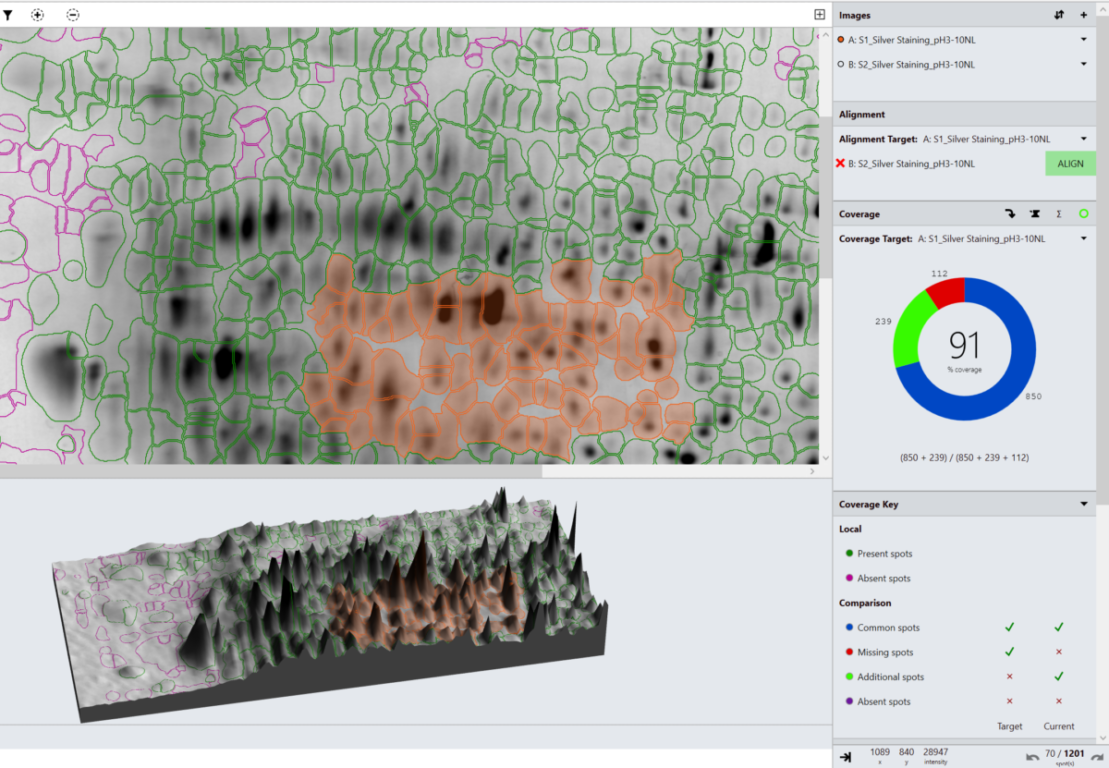
2D Electrophoresis + Western Blotting (e.g., 2D-PAGE, 2D-DIGE, 2D-DIBE):
This approach provides a visual profile of HCPs, enabling validation of antibody coverage for ELISA. When combined with software such as TotalLab’s SpotMap 2D, these techniques allow accurate, reproducible coverage analysis aligned with 21 CFR Part 11 and GMP standards.
LC-MS (Mass Spectrometry):
Used for its ability to detect low-abundance HCPs with high resolution. When integrated with TotalLab’s SpotMap MS, scientists can automate and streamline large-scale HCP characterization workflows.
Challenges in HCP Analysis
Each method has its own set of strengths and limitations and it’s for that reason that it’s recommended to use a combination of different techniques (referred to as “orthogonal” techniques) for your HCP analysis:
ELISAs, whilst robust, require careful validation to confirm sufficient antibody coverage (through something like the the 2D techniques mentioned above) to make sure they’re actually capturing a wide array of the HCP’s present in your sample. This lack of specificity also highlights another limitation of the technique – your ELISA can only report a total HCP concentration rather than the concentration of specific HCPs. Latest research in the field confirms that not all HCPs represent the same risk to patients or to the stability of your biotherapeutic and so it’s crucial to know the identity of your HCPs to determine acceptable limits within your final drug substance. For example, 1 PPM of one HCP may be perfectly acceptable within your final drug substance but for another it could be extremely dangerous to patients.
2D-PAGE and Western blotting techniques (including 2D-DIGE, 2D-DIBE) being image based techniques can suffer from high inter-operator variability (if steps like automatic spot detection or alignment are performed manually) however allow users to visualize and characterize their antibody specificity which is especially useful for bridging assays when moving from one lot of reagents to another. Another downside of 2D-based techniques is they’re extremely time consuming to perform and analyze (although our SpotMap 2D software allows the coverage score portion of this analysis to be performed much quicker than usual).
and LC-MS, though powerful, demands time-consuming sample prep and complex data analysis. Detecting and quantifying HCP residues in samples is difficult especially when your HCP concentration is significantly lower than your drug substance. The process of preparing samples for LC-MS analysis is made more complicated by the need to remove specific proteins like monoclonal antibodies. This requires a large amount of the starting material, and the process is time-consuming and labor-intensive. Additionally, it can’t be used to analyze multiple preparations at the same time.
TotalLab attempts to minimize these limitations using intelligent software – purpose-built, automated software that enhances consistency between operators and accelerates HCP analysis across sites and teams.
Future Outlook and Risk Management
The major challenge, both now and into the future, in analyzing HCP content in biotherapeutics is being able to accurately determine the level of each HCP present in your drug substance. Ideally, it would be possible to perform this analysis during the production process to track impurities and be warned of their presence throughout the stages of production however as mentioned above, a number of the current gold-standard techniques require a significant time investment to provide results which isn’t feasible during production. This means that we’re left to perform HCP analysis at the end of production on the finished product, meaning that if HCPs are present at unacceptable levels the whole batch needs to be discarded.
As biologics become more complex, so does the need for precision in HCP detection. Tools that support longitudinal data review, automate compliance reporting, and enable collaborative workflows are becoming indispensable. TotalLab’s suite of solutions—from ELISA analysis to 2D and LC-MS quantification—provides scalable, validated platforms to help life science teams manage this growing complexity while meeting global regulatory expectations.