Western Blot Troubleshooting Guide

Western Blot Troubleshooting Guide
Western blotting is a crucial technique used in molecular biology to detect specific proteins in a sample. However, troubleshooting Western blot images can be challenging due to various potential issues that can arise during the process. This article will guide you through the best methods to troubleshoot common problems encountered in Western blotting, ensuring clear and quantifiable results.
Common Issues in Western Blotting
Several common problems can affect the quality of Western blot images and prevent accurate quantification, including:
- No/Low signal
- High background noise
- Non-specific bands
- Uneven bands or smears
Understanding these issues is the first step in troubleshooting and obtaining clear results, our 1D analysis software Phoretix 1D includes tools to minimise the impact of these common problems to allow you to still obtain reliable, quantifiable data even from poor quality images. This means less time spent repeating experiments and less money wasted on additional reagents.
Troubleshooting Guide
No Signal
Causes:
- Poor transfer efficiency
- Antibody-related specificity problems
- Low protein concentration
Solutions:
- Check Transfer Efficiency: Ensure that the protein transfer from the gel to the membrane was successful. To do this, stain the membrane with a non-specific protein stain like Ponceau S to confirm the presence of proteins:

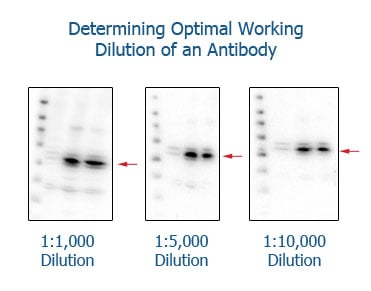
- Optimize Antibody Concentration: Use the recommended dilution for primary and secondary antibodies. Too high or too low concentrations can affect signal detection.

- Increase Protein Load: If the protein concentration in the sample is low, increase the amount of sample loaded onto the gel.
High Background
Causes:
- Non-specific binding of antibodies
- Inadequate blocking
- Insufficient washing
Solutions:
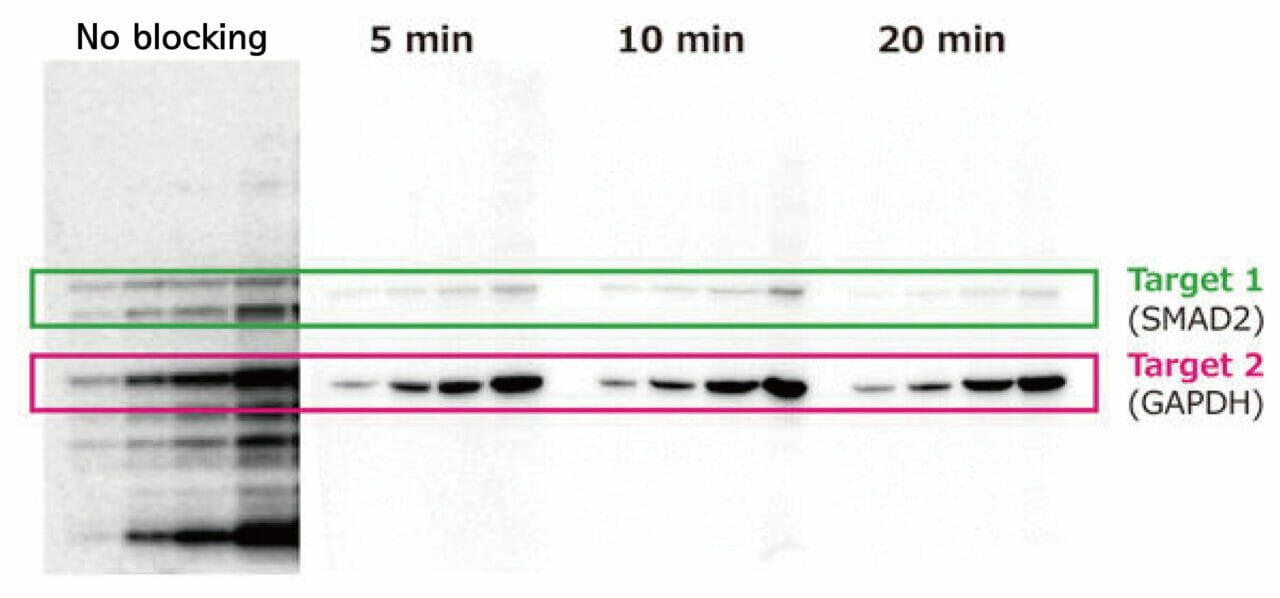
- Optimize Blocking Conditions: Use appropriate blocking agents (e.g., 5% BSA or non-fat dry milk) and ensure sufficient blocking time.

- Improve Washing Steps: Increase the number and duration of washing steps to remove unbound antibodies. Use a gentle detergent like Tween-20 in the wash buffer.
- Reduce Antibody Concentration: Excessive antibody can lead to high background. Optimize the concentration to balance signal and background.

Non-Specific Bands
Causes:
- Cross-reactivity of antibodies
- Overloading of protein
Solutions:
- Use Specific Antibodies: Ensure that primary and secondary antibodies are specific to the target protein. Pre-adsorption with the blocking agent can reduce non-specific binding.
- Optimize Protein Load: Avoid overloading the gel with too much protein, which can cause non-specific bands.

Uneven Bands
Causes:
- Inconsistent gel polymerization
- Uneven transfer
- Sample preparation issues
Solutions:
- Ensure Even Gel Polymerization: Prepare gels with care to ensure uniform polymerization. Use fresh reagents and follow standard protocols.

- Check Transfer Uniformity: Confirm that the transfer apparatus is functioning correctly and that the membrane is evenly placed.

- Improve Sample Preparation: Ensure that samples are adequately prepared and homogenized. Avoid air bubbles when loading the gel.

Preventative Measures
- Use Fresh Reagents: Ensure all reagents are fresh and properly stored.
- Regular Equipment Maintenance: Regularly check and maintain all equipment used in the process.
- Standardize Protocols: Use standardized protocols and document any deviations to identify potential sources of error.
Conclusion
Troubleshooting Western blot images involves a systematic approach to identify and rectify common issues such as no signal, high background, non-specific bands, and uneven bands. By understanding the underlying causes and applying targeted solutions, researchers can improve the quality and reliability of their Western blot results. Regular maintenance of equipment, optimization of protocols, and careful preparation of reagents are essential for consistent success in Western blotting.
By following these guidelines, you can optimize your Western blotting technique, leading to clearer results and better quality quantifiable data.. For further reading and additional tips, explore our comprehensive guides and tutorials available online or on our YouTube channel here.